Gate Control Hypothesis . 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. The gate control theory of pain (fig. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose.
from www.spine-health.com
This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. The gate control theory of pain (fig. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting.
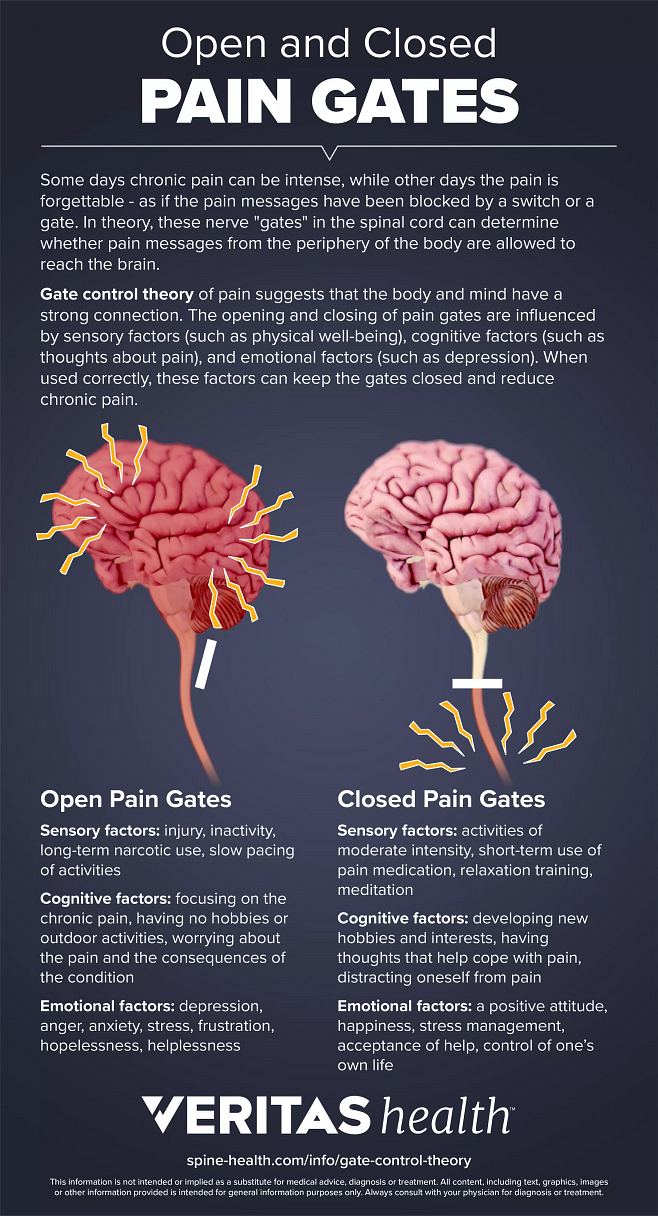
The Gate Control Theory of Chronic Pain Infographic Spinehealth
Gate Control Hypothesis gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. The gate control theory of pain (fig. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain.
From study.com
Gate Control Theory of Pain Definition, Examples & Application Lesson Gate Control Hypothesis 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From health.clevelandclinic.org
Pain and the Brain What Is the Gate Control Theory? Cleveland Clinic Gate Control Hypothesis a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From wisc.pb.unizin.org
Somatosensory Receptors KINES 200 Introductory Neuroscience Gate Control Hypothesis a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.spine-health.com
The Gate Control Theory of Chronic Pain Infographic Spinehealth Gate Control Hypothesis the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. 7.1) was developed by. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From spearmoreabout.blogspot.com
gate control theory Gate Control Hypothesis a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. 7.1) was developed by. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.science.org
GateControlled Superconducting Proximity Effect in Carbon Nanotubes Science Gate Control Hypothesis the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From slidetodoc.com
DIADYNAMIC CURRENTS BY ABDULLAH RADWAN Diadynamic currents They Gate Control Hypothesis The gate control theory of pain (fig. the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.researchgate.net
GateControl Theory (figure from Melzack, 1993) Download Scientific Diagram Gate Control Hypothesis the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.youtube.com
Physiology of Pain and Gate Control Theory YouTube Gate Control Hypothesis 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. The gate control theory of pain (fig. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.mdpi.com
Micromachines Free FullText Mathematical Model for Skin Pain Sensation under Local Gate Control Hypothesis 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. The gate control theory of pain (fig.. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From techcommunity.microsoft.com
Quantum Gates and Circuits The Crash Course Microsoft Community Hub Gate Control Hypothesis The gate control theory of pain (fig. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.researchgate.net
(PDF) Proposed New Pathophysiology of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Gate Control Hypothesis the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate'. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From amazonia.fiocruz.br
Custom Essay amazonia.fiocruz.br Gate Control Hypothesis a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. The gate control theory of pain (fig. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.science.org
Quantum Hall Effect in a GateControlled pn Junction of Graphene Science Gate Control Hypothesis gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. The gate control theory of pain (fig. a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From ebrary.net
The Gate Keeping Procedures for Null Hypothesis Testing with Multiple Variables Gate Control Hypothesis the gate control theory of pain, proposed by melzack and wall in 1965, offers a framework for understanding this interplay, suggesting. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a neurobiologist and a psychologist who wanted to propose. The gate control theory of pain (fig. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From mungfali.com
Gate Control Theory Diagram Gate Control Hypothesis a major prediction of the gate control hypothesis was that enhancing input. The gate control theory of pain (fig. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues.. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Nociceptive sensation. PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3747968 Gate Control Hypothesis This theory is often used to explain both phantom and chronic pain issues. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. the gate control theory of pain,. Gate Control Hypothesis.
From www.liverpool.ac.uk
Pain Gate Control Hypothesis The gate control theory of pain (fig. gate control theory suggests that the spinal cord contains a neurological 'gate' that either blocks pain signals or allows them to continue on to the brain. 7.1) was developed by melzack and wall in 1965 and is the most. the gate control theory of pain was formulated in 1965 by a. Gate Control Hypothesis.